Model Context Protocol
- The Universal Interface for AI and Tools
Imagine you arrive in California after a long trip from Germany and try to charge your phone. Good luck! 😏 The plug doesn't fit because it doesn't comply with our European standards. You need a travel adapter, a bridge between your phone charger and the power outlet in California. The analogy might be very abstract, but in my eyes, MCP can be seen as a universal adapter for artificial intelligence. MCP stands for Model Context Protocol, and the general idea is to create a standard that allows AI systems to communicate with tools and data sources.
Interestingly, MCP has recently experienced a surge in public perception, even though its introduction already happened in November 2024. According to Google Trends, interest in Germany increased in recent weeks in October 2025, so we can see that MCP is moving more into the focus of the AI community.
See here what the current trend is. Is the trend today still the same?
Let's check the 'why' behind this MCP 🧐.
Anthropic realized soon that with N different AI models
and the interaction with M different tools,
the number of individual interfaces grows fast. The maintenance effort would be difficult, and
scalability would be low.
For example, if we wanted to link 10 AI models with 120 tools, that would be N × M = 10 × 120 = 1200 individual connections.
MCP solves this problem through a standardized communication path, so that we only need N + M = 130 connections.
The Roles in MCP
The MCP architecture involves the following roles:
- MCP Host - The user interface (e.g., Claude Desktop)
- MCP Client - Data exchange
- MCP Server - Tools and data the AI can work with
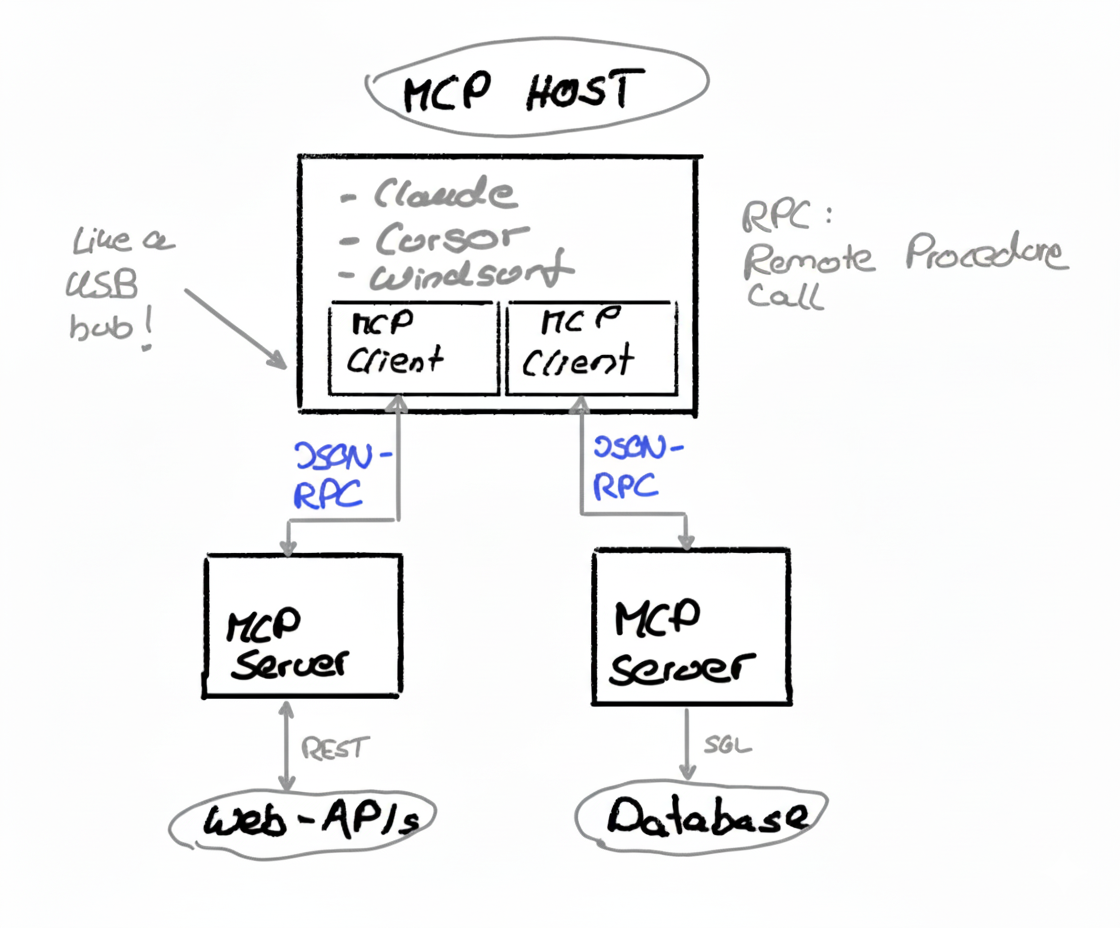
In the following, we show an illustration of the architecture. We have the MCP Host (e.g., Claude, CURSOR,
Windsurf), and within the host are the MCP Clients.
The Clients communicate via JSON-RPC (Remote Procedure Call) to an MCP Server that is connected to different
tools, such as databases or Webservices. JSON-RPC is different from REST; it always includes the name of the function that should be called with additional, necessary parameters.
Anthropic also compares an MCP Host with a USB hub: each USB port in the USB hub is an MCP Client that can be
connected to different hardware (mouse, keyboard, external hard disk).
Claude Desktop as Host + MCP Server in n8n
Let's set up Claude Desktop and an MCP Server in n8n. To do this, three steps are necessary, plus testing as the fourth step (I almost forgot 🧐).
1.1 Open Configuration File
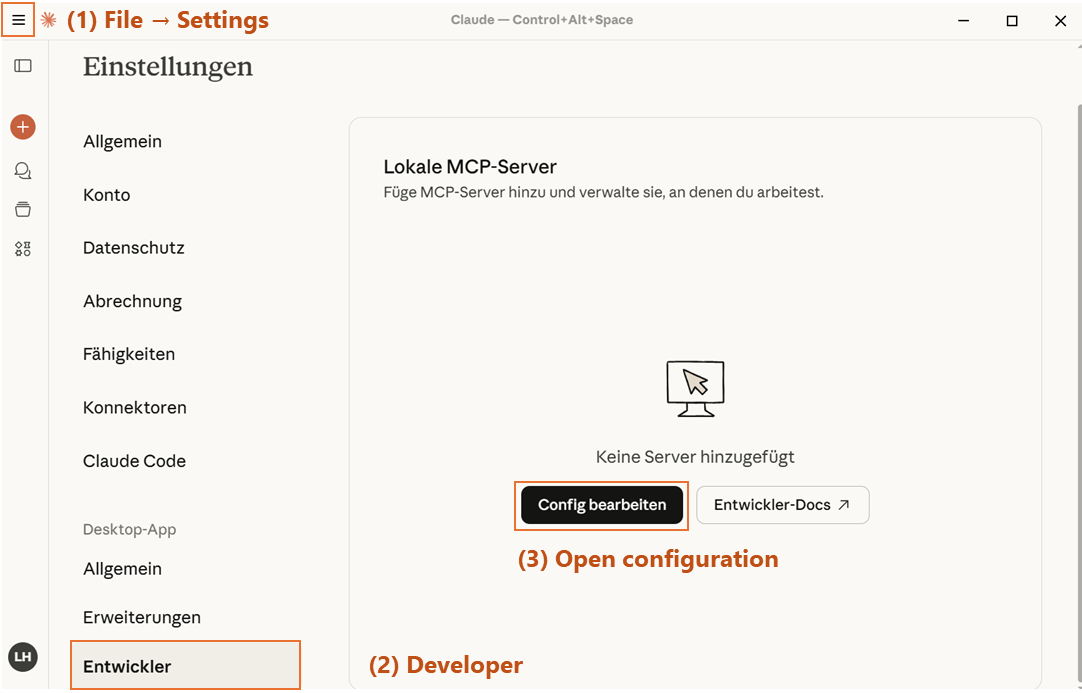
Open Claude Desktop. Click on the hamburger menu in the upper-left corner. Go to the menu option for 'File' and select 'Settings'. In the settings, scroll down until you see 'Developer'. Then click on 'Edit config'. Check out the following screenshot - the labels are in German, but the structure is identical in every language. The steps are marked with numbers.
1.2 Edit MCP Configuration
Open the displayed configuration file and insert the following configuration for accessing the n8n MCP Server. For example, use this structure:
{
"mcpServers": {
"n8n": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"supergateway",
"--sse",
"XYZ"
]
}
}
}
You need to replace XYZ with the production URL of
your MCP Server trigger node. Interested in what the arguments mean? Then ask Claude!
1.3 MCP Server
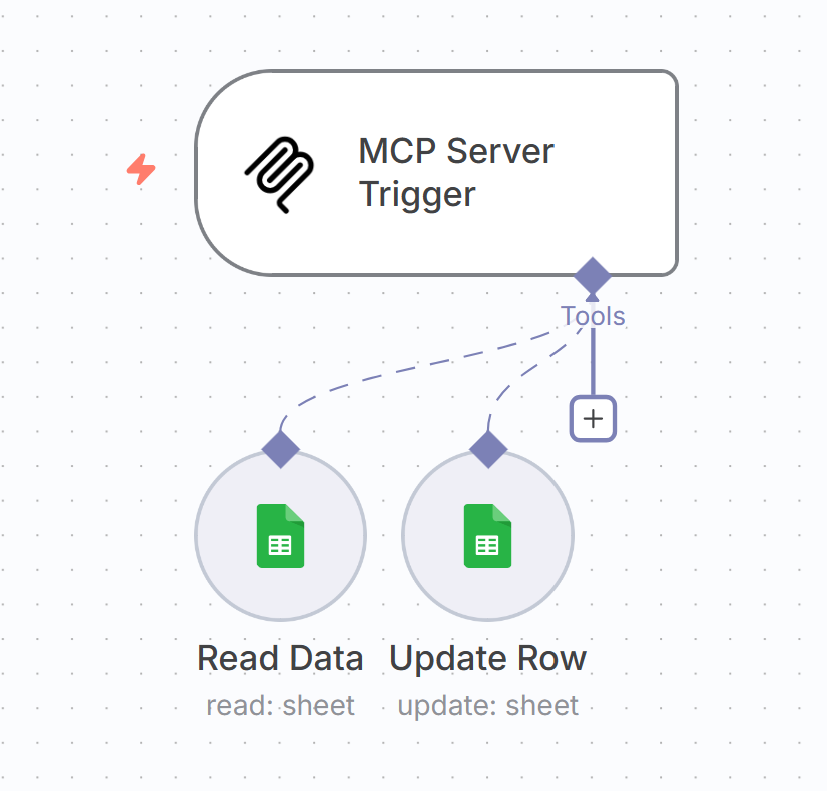
For the last step, we need to set up our MCP Server using n8n. Here we use an example MCP Server with
two tools: one for reading data from a CSV file (e.g., in Google Sheets) and one for updating the data in the CSV file.
Our use case is to update the status of products being sold on eBay.de.
Here you can download our small
example workflow:
Download example workflow
1.4 Testing
Testing is always good. Let us start. First of all, if we add a new tool or function to the workflow, we need to reload the MCP configuration file. Once it is loaded successfully, we will see our tools in the tool section.
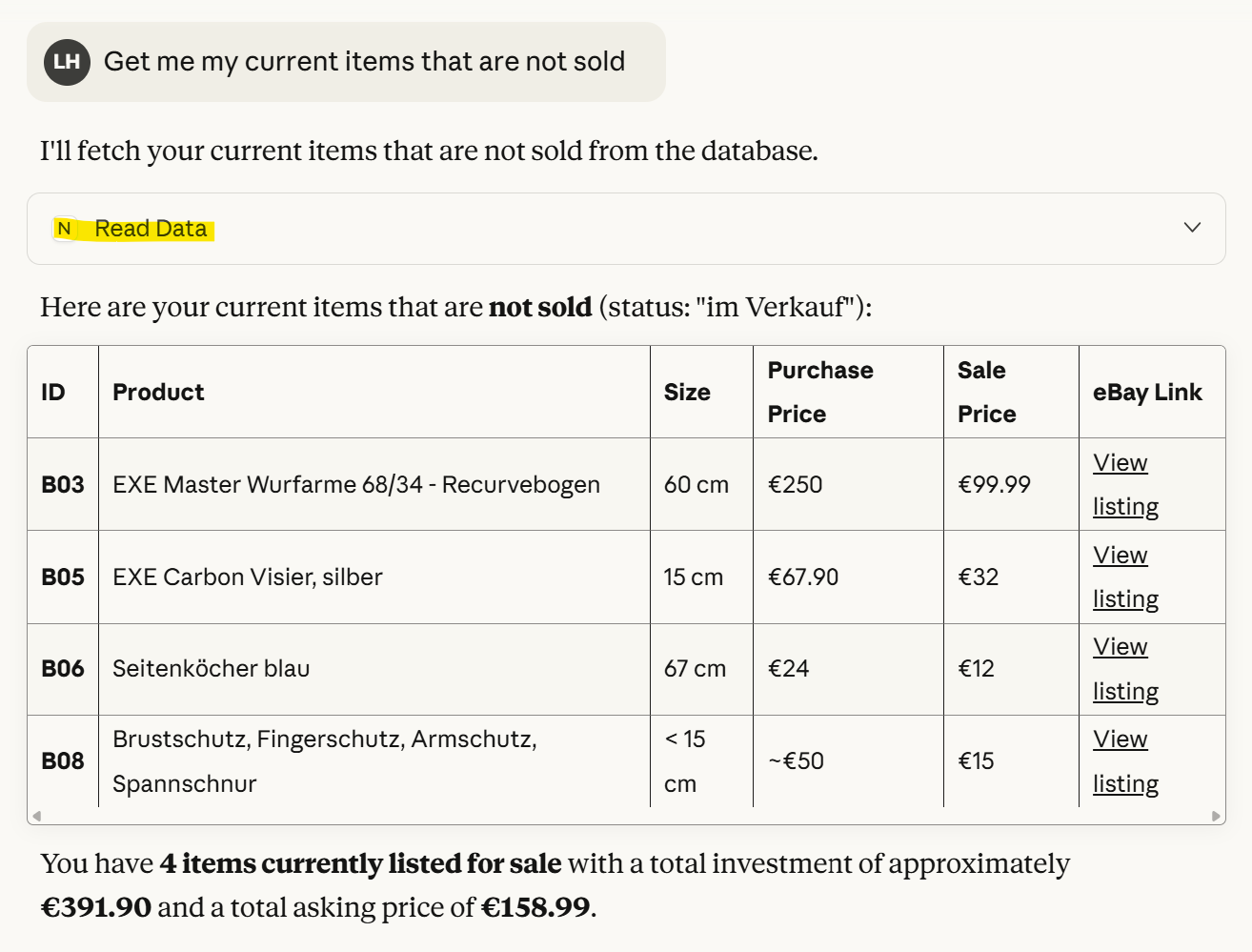
Let us try the following prompt: 'Get me my current items that are not sold'. After giving permission, Claude will read the items that are not sold from my CSV data. In this case, the data refers to old archery equipment I used when I was interested in this sport.
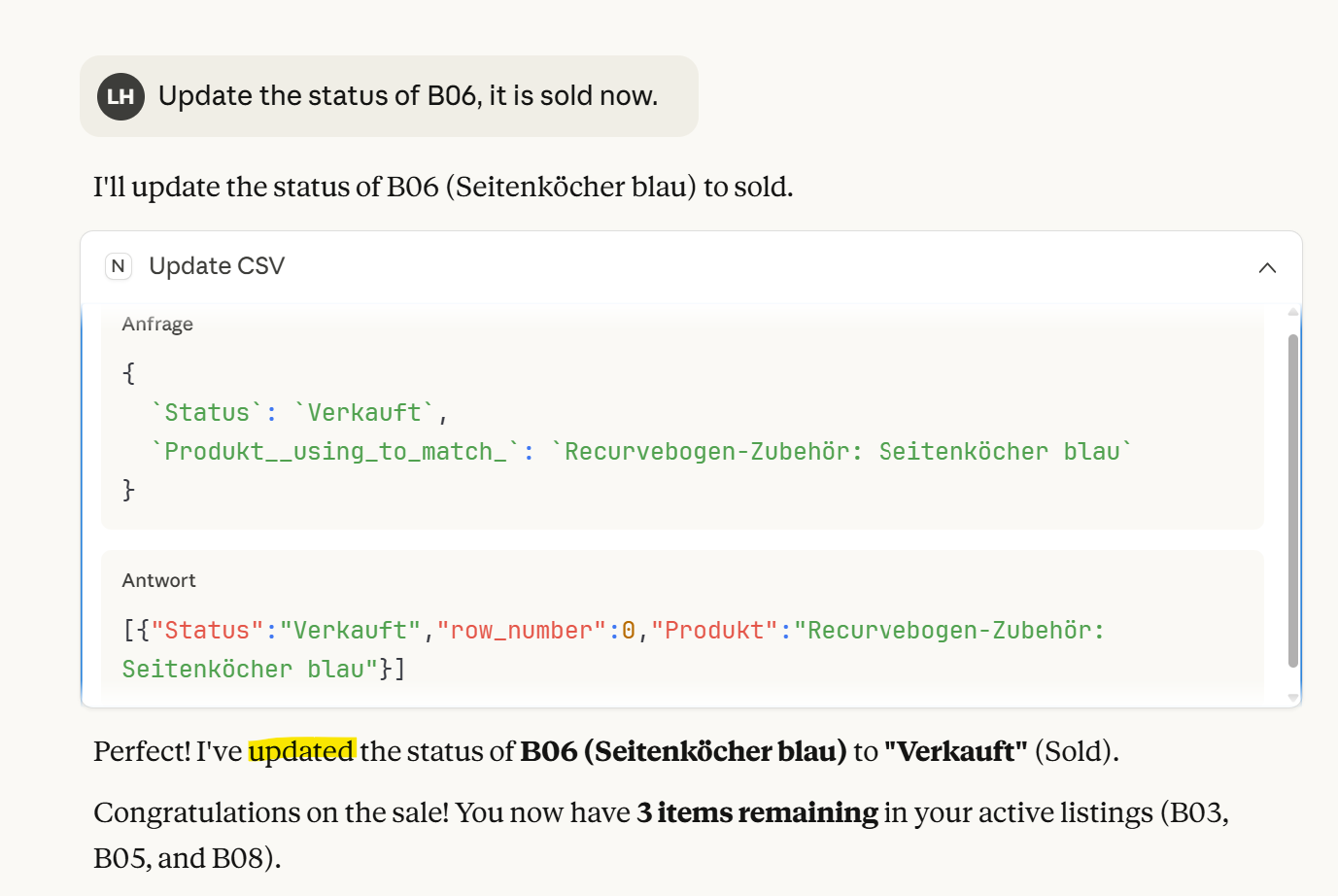
Let us try to update one status with the prompt: 'Update the status of B06; it is sold now'. Claude will update the status in my CSV data. You can also see the request and the response when you open the dropdown menu.
This is great - isn't it? 🥳🚀🍀
Summary
The Model Context Protocol serves as a universal adapter to standardize communication between a growing
number of AI models and tools.
It solves the scalability problem of countless individual interfaces. With the division into Host (AI),
Client (connection), and Server (tools),
a robust architecture is created. Setup in applications like Claude Desktop is possible in just a few
steps via Developer Mode and editing a configuration file.
There are of course more applications that support MCP integrations, see the following link:
List of applications supporting MCP integrations
Stay tuned for more articles! 🤖